AI-enabled virtual spatial proteomics from histopathology for interpretable biomarker discovery in lung cancer
 HEX: AI-enabled virtual spatial proteomics.
HEX: AI-enabled virtual spatial proteomics.Abstract
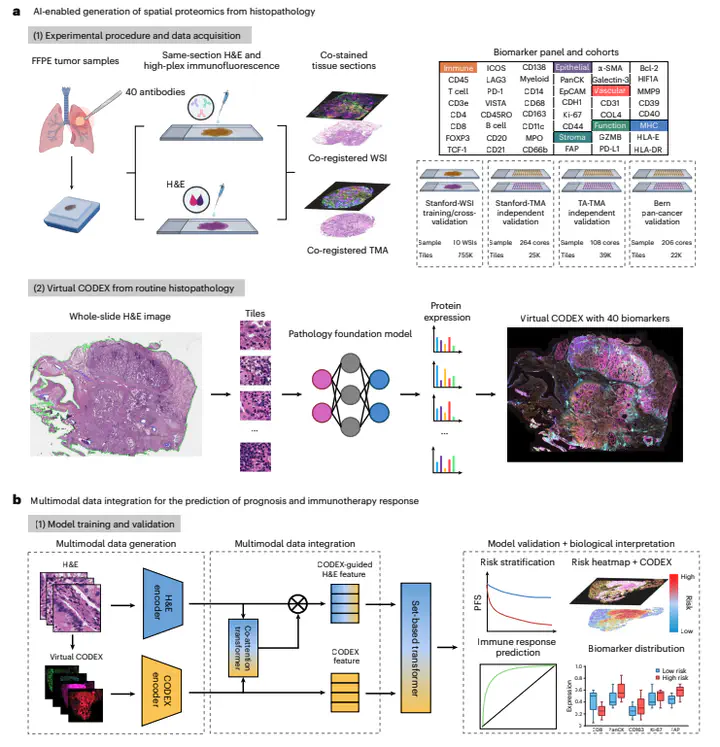
Spatial proteomics enables high-resolution mapping of protein expression and can transform our understanding of biology and disease. However, major challenges remain for clinical translation, including cost, complexity and scalability. Here we present H&E to protein expression (HEX), an AI model designed to computationally generate spatial proteomics profiles from standard histopathology slides. Trained and validated on 819,000 histopathology image tiles with matched protein expression from 382 tumor samples, HEX accurately predicts the expression of 40 biomarkers encompassing immune, structural and functional programs. HEX demonstrates substantial performance gains over alternative methods for protein expression prediction from H&E images. We develop a multimodal data integration approach that combines the original H&E image and AI-derived virtual spatial proteomics to enhance outcome prediction. Applied to six independent non-small-cell lung cancer cohorts totaling 2,298 patients, HEX-enabled multimodal integration improved prognostic accuracy by 22% and immunotherapy response prediction by 24–39% compared with conventional clinicopathological and molecular biomarkers. Biological interpretation revealed spatially organized tumor–immune niches predictive of therapeutic response, including the co-localization of T helper cells and cytotoxic T cells in responders, and immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophage and neutrophil aggregates in non-responders. HEX provides a low-cost and scalable approach to study spatial biology and enables the discovery and clinical translation of interpretable biomarkers for precision medicine.